What Just Happened?
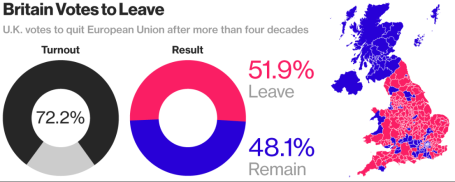
Breakups are never easy, especially when they come as a surprise. That’s exactly what happened with last week’s “Brexit” (British exit) referendum results. History was made when 51.9% of the United Kingdom (U.K.) voters from England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland cast their vote to divorce (“Leave”) their country from the European Union (EU). In the end, the 48.1% of U.K. voters could not generate enough support to “Remain” in the EU (see chart below). Despite torrential downpours in southern Britain, voter turnout was extraordinarily high, as 72% of the 46.5 million registered voters came out in full force to have their voices heard.
Divorce is never cheap, and UK Prime Minister David Cameron paid the ultimate price with his defeat in the Brexit referendum…the loss of his job. Immediately following the release of the referendum results, Cameron, the British Prime Minister since 2010 and leader of the Conservative Party, immediately announced his resignation, effective no later than October 2016 after the selection of his successor.
One of the reasons behind the shock of the Brexit Leave decision is the longstanding relationship the U.K. has had with the EU. European Union membership first began in 1957 with Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, Luxembourg, and Netherlands being the founding countries of this new political-economic union.
A few decades later, the U.K. officially joined the EU in 1973 with Ireland and the Denmark, shortly before Margaret Thatcher came into power. If you fast forward to today, some 43 years after U.K. originally joined the EU, the Brexit decision represents the largest turning point in European political history. Not since the 1989 falling of the Berlin Wall and the subsequent demise of the Cold War in the Soviet Union has such a large, earth-moving political shift occurred.
Today, there are 28 member countries in the EU with Croatia being the newest member in 2013. Despite the Brexit outcome, there still is a backlog of countries wanting to join the EU club, including Turkey, Serbia, Albania, and Montenegro (and this excludes Scotland, which has voiced an interest in leaving the U.K. for the EU).
What Were Investors’ Reactions?
Financial markets around the world were caught off guard, given many pre-referendum polls were showing the Remain camp with a slight edge, along with British betting parlors that were handicapping an overwhelming victory for the Remain camp. Here’s a summary of stock market reactions around the globe from June 23rd to June 30th:
U.S. (S&P 500): -0.7%
U.K. (FTSE 100): +2.6%
Japan (Nikkei): -4.1%
Germany (DAX): -5.6%
Hong Kong (Hang Seng): +0.4%
China (Shanghai Composite): +1.3%
India (BSE): -0.0%
Surprisingly, modest monthly gains achieved in the S&P 500 prior to the Brexit vote (up +0.8%) were quickly pared after the results came in but remained positive for the entire month (up +0.1%). For the year, U.S. stocks are up a limited +2.7%, which isn’t too bad considering investors’ current mood.
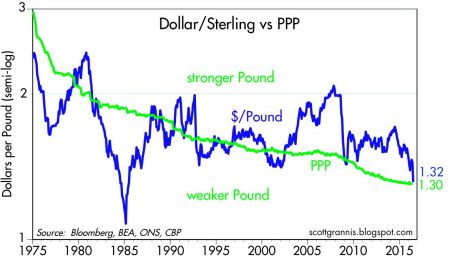
Stocks were not the only financial market disrupted after the Brexit announcement, foreign exchange currency rates were unstable as well. The British pound dived to a 30-year low shortly after the vote to a level of approximately $1.33/£, and was down more than -10% on the day of the announcement. UK banks like Barclays (LON:BARC) PLC (BCS) and Lloyds Banking Group (LON:LLOY) also saw their share prices significantly pressured as EU regulatory risks of losing access to European customers and negative global interest rates further squeeze the banks’ profit margins.
To put the currency picture into perspective, the value of the British pound ($2.64/£) peaked in March 1972 at a rate about double the U.S. dollar today. On the positive side of the ledger, a weaker British pound could help boost exports and vacation time to Stonehenge or London, but there is also a risk for a spike of inflation (or stagflation) on the country’s roughly $740 billion in imports (e.g., food, energy, and raw materials).
Why Did it Happen?
While economically prosperous regions like London and Scotland voted heavily for Remain, the message for change of the Leave camp resonated well with working class towns and rural areas of England. Besides a geographic split, there was also a demographic divide between voters. As you can see from the YouGov poll below, the majority of younger citizens overwhelmingly voted for Remain, and vice versa for older citizens as it relates to the Leave vote.
18-24: 75% Remain
25-49: 56% Remain
50-64: 44% Remain
65+: 39% Remain
While geography and demographics certainly played a key role in the outcome of the EU Leave referendum result, at the core of the movement also was a populist discontent with immigration and the negative economic consequences created by globalization. There are many reasons behind the sluggish economic global recovery, even if the U.S. is doing best out of the developed countries, but rightly or wrongly, immigration policies and protectionism played a prominent part in the Brexit.
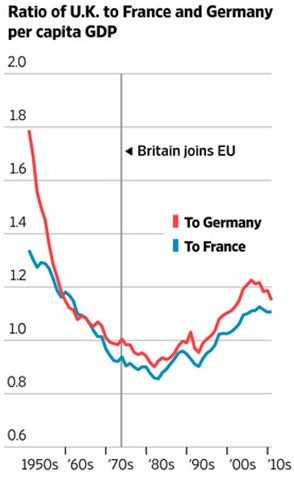
At the heart of the populist sentiment of lost control to Brussels (EU) and immigration is the question of whether the benefits of globalization have outweighed the costs. The spread of globalization and expanded EU immigration has disenfranchised many lower skill level workers displaced by eastern European immigrants, Syrian refugees and innovative solutions like automated machinery, software, and electronic equipment. Economic history clearly shows the answer to the effectiveness of globalization is a resounding “yes”, but the post-financial crisis recovery has been disappointingly sluggish, so a component of the populist movement has felt an urgency to find a scapegoat. The benefits of globalization can be seen in the chart below, as evidenced by the increases in per capita GDP of the UK relative to Germany and France, after joining the EU in 1973. Many observers are quick to identify the visible consequences of globalization (i.e., lower-paying job losses), but fail to identify the invisible benefits (i.e., productivity, lower prices, investment in higher-paying job gains).
What happens next?
While some EU leaders want to accelerate the Brexit transition, in actuality, this will require a long, drawn-out negotiation process between the still-unnamed new UK Prime Minister and EU officials. The complete EU-Brexit deal will take upwards of two-years to complete, once Article 50 of the EU Lisbon Treaty has been triggered – likely in October.
In light of the unchartered nature of the Brexit Leave vote, nobody truly knows if this decision will ultimately compromise the existential reality of the EU. Time will tell whether Brexit will merely be a small bump on the long EU road, or the beginning of a scary European domino effect that causes the 28 EU country bloc to topple. If the U.K. is successful in negotiating EU trade agreements with separate European countries, the Brexit even has a longer-term potential of benefiting economic activity. Regardless of the EU outcome, the long-term proliferation of capitalism and democracy is likely to prevail because citizens vote with their wallets and capital goes where it is treated best.
What does Brexit Mean for Global Markets?
The short answer is not much economically, however there have been plenty of less substantial events that have roiled financial markets for relatively short periods of time. There are two basic questions to ask when looking at the economic impact of Brexit:
1) What is the Brexit impact on the U.S. economy?
If you objectively analyze the statistics, U.S. companies sold approximately $56 billion of goods to the U.K. last year. Even if you believe in the unlikely scenario of a severe U.K. economic meltdown, the U.K. trade figure is a rounding error in the whole global economic scheme of things. More specifically, $56 billion in trade with the U.K. equates to about .003 of the United States’ $18+ trillion GDP (Gross Domestic Product).
2) What is the Brexit impact on the global economy?
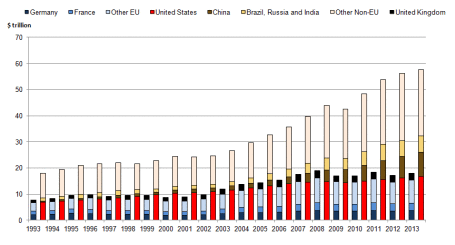
The U.K.’s GDP amounts to about $3 trillion dollars. Of that total, U.K. exports to the EU account for a reasonably insignificant $300 billion. As you can see from the chart below, $300 billion in UK exports to the EU are virtually meaningless and coincidentally equate to about .003 of the world’s $78 trillion estimated GDP.
What to Do Next?
Like many divorces, the U.K. Brexit may be messy and drawn out, until all the details are finalized over the next couple years. It’s important that you establish a strong foundation with your investments and do not divorce the sound, fundamental principles needed to grow and preserve your portfolio. As is usually the case, panicking or making an emotional decision relating to your investments during the heat of some geopolitical crisis rarely translates into an optimal decision over the long-run. As I repeatedly have advised over the years, these periods of volatility are nothing new (see also Series of Unfortunate Events).
If you catch your anxiety or blood pressure rising, do yourself a favor and turn off your TV, radio, or electronic device. A more productive use of time is to calmly review your asset allocation and follow a financial plan, with or without the assistance of a financial professional, so that you are able to achieve your long-term financial goals. This strategy will help you establish a more durable, long-lasting, and successful marriage with your investments.
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in certain exchange traded funds (ETFs), but at the time of publishing had no direct position in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision.
