The $5.1 billion deal to buy the Costa Coffee chain by Coca-Cola (NYSE: NYSE:KO) is just the latest example highlighting the great lengths to which food and drink companies are trying to keep pace with rapidly changing consumer habits that are upending traditional business models across the sector.
The former owner, Britain's Whitbread (LON:WTB), had said it would spin off Costa, the world's second largest coffee shop chain after Starbucks (NASDAQ:SBUX). But the price Coke offered for Costa was simply too good to pass up.
For Coca-Cola, the transaction represents a full-fledged leap into the global coffee market, where it has little presence currently. “Hot beverages is one of the few remaining segments of the total beverage landscape where Coca-Cola does not have a global brand,” said James Quincey, president and CEO of Coke. “Costa gives us access to this market through a strong coffee platform.”
This move continues Coke's process of diversifying away from the fizzy and sugary drinks that made the company famous. These type of drinks have declined in popularity among increasingly health-conscious consumers. The deal is all part of the company’s effort to reposition itself as a “total beverage company”. As Mr. Quincey said, coffee was among the “strongest growing [beverage] categories in the world” and the company was missing out.
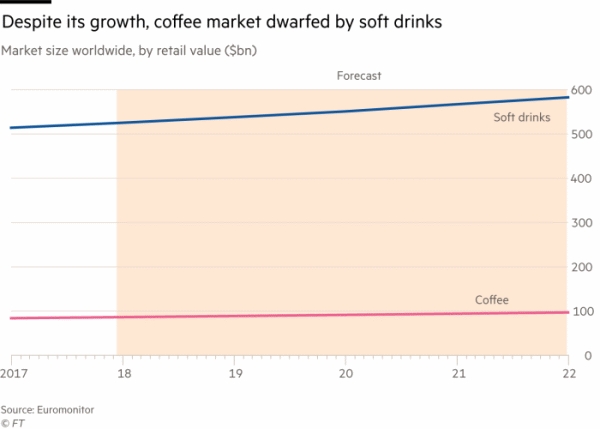
As the chart above shows, the potential for growth of coffee beverages versus soft drinks is high. So with Coke now entering the market, it sets up a battle royal for coffee sales between the world’s biggest beverage maker and the other giants in the sector including Starbucks, Nestlé (OTC:NSRGY) and privately-held JAB Holdings. More on that later.
Consumer Drinks Pressure
Coke's proposed transaction is just the latest in a series by established consumer brands, which are taking divergent approaches in response to the demand from consumers globally for fresher and healthier products.
Some consumer companies are expanding into territories or products with brighter growth prospects. Coke's arch-rival PepsiCo (NASDAQ:PEP) recently struck a $3.2 billion deal to buy Sodastream (NASDAQ:SODA), which makes home carbonation products. This deal came mere days after Coke agreed to buy a minority stake (with a path to full ownership) in BodyArmor, a sports drink maker backed by US basketball star Kobe Bryant.
Coke has struggled for years to loosen the hold of Pepsi’s sports drink Gatorade business, with its Powerade drink. But it may have struck gold with BodyArmor. Its products use coconut water, have higher levels of potassium than its competitors, do not use artificial colors, allowing the company to market its products as a healthier alternative to Gatorade and Powerade. Now it will gain access to Coca-Cola’s bottling system, allowing it to increase production.
The research firm Euromonitor said that sports drinks volumes were flat last year in the U.S., as both of the big two brands struggled. The one real exception, according to Euromonitor, was BodyArmor. Analysts with Wells Fargo, relying on Nielsen data, estimated that Body Armor retail sales had climbed 90% over the past year to $288 million. Much of that market share came from Gatorade.
Both Coke and Pepsi are coming under increasing pressure from JAB Holding, a Luxembourg-based investment vehicle backed by the billionaire Reimann family. As part of its international buying spree JAB bought the Keurig Green Mountain coffee business, best known for its single-serve brewing machines, in December 2015 for $13.9 billion. And JAB made a more direct threat to the two incumbents when, in January 2018, it struck a $18.7 billion deal to acquire Dr. Pepper Snapple and combined it with Keurig to create a beverage group with almost $11 billion in annual revenue.
The Steaming Hot Coffee Market
Once you get to the global coffee market, the competition gets even hotter as global food and beverage giant Nestle is a major player. Its recent deals in the space include acquiring the rights to sell Starbucks products and taking a majority stake in roaster Blue Bottle.
According to Euromonitor, the global coffee industry is valued at more than $80 billion, and has been expanding at an annual rate of more than 5%. Here in the United States – the world’s biggest coffee market – most of the growth is coming from a resurgence in the café culture among millennials aged 18 to 34.
According to a recent survey conducted by the National Coffee Association, 15% of millennials had their last cup of coffee in a café and 32% had an espresso-based drink the day before the survey, the highest share for any age group. These are the type of consumers Coke is trying to reach through its purchase of Costa.
This data is also why Dunkin Brands (NASDAQ:DNKN) is Wall Street's hottest takeover target, sending its stock to all-time highs. Dunkin is a lot more than a donut shop today and has pushed into more upmarket coffee offerings such as cold brew and espresso drinks. It will likely be added to the $250 billion in deals in the coffee business over the past six years.
But what about Coca-Cola? Was the purchase of Costa a smart move?
Coke and Coffee
Not surprisingly, I am once again in disagreement with the Wall Street consensus. They hate the deal and I love it.
Analysts are saying that Coke knows nothing about brick-and-mortar stores even though Coke insists “this is a coffee strategy, not a retail strategy.”
Maybe the analysts are right, but they are ignoring that the entire Costa team is staying in place. When Whitbread bought Costa in 1995 it was a company that was just a small chain of 39 cafes across Britain to today having 2,400 shops in Britain and another 1,400 in more than 30 countries with a brand that is recognized in most parts of the world.
Costa has recently begun its push into China, where it pitches its drinks to Chinese consumers as a luxury treat. It still has only 460 shops there, so the potential for growth is enormous. Starbucks has 600 shops in Shanghai alone.
Costa just did not have the financial firepower for a major push into China, but now with Coke's financial muscle, it does. It will help too that surveys show Chinese consumers consider Costa to be of higher quality than Starbucks. And the trade war may play right into Costa's hands if Chinese consumers begin boycotting American products.
And I like the deal for its symmetry. Think about it – Coke started out being served as a flavor of syrup in the soda fountains of little neighborhood stores (drug stores, etc.) in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The soda was mixed by black-tied “soda jerks” behind marble counters – the forerunners of today's baristas. Then Coke completely moved away from direct contact with consumers…
But now it's back with Costa's coffee houses and its baristas. Just for nostalgia's sake, I hope they succeed. And they might – after all, Amazon (NASDAQ:AMZN) had little brick-and-mortar experience before it bought Whole Foods and Apple (NASDAQ:AAPL) does have its physical stores. Coke going back to its roots looks like a winner to me.