This week, I am participating in a school-style debate at the Global Fixed Income Institute’s conferences in Madrid where the question before the house is whether or not inflation will resurface in major world economies in the next five years. As you might imagine, I feel that my part of the debate is the easy part, especially as inflation is pointing higher in the US and core inflation just surprised higher in Europe. However, I am sure the other side feels the same way.
The Institute is interested in this discussion partly to illuminate the question of whether the substantial rise in yields over the last three months or so in all developed bond markets (see chart, source Bloomberg, showing 10y yields in U.S., UK, Germany and Japan) is indicative of a return of fears of inflation.
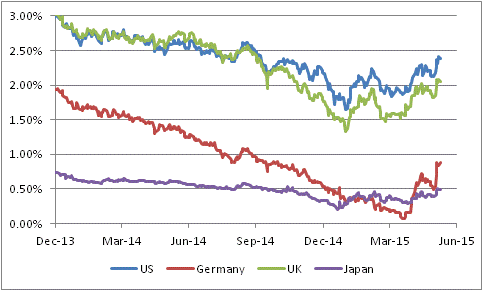
The ironic part of this is that I do not believe that the rise in yields has much, if anything, to do with the expectation for higher inflation. Partly, it is due to a subtle sea change in the way investors are thinking about the prospects for central bank policy – to wit, the possibility (which I see as slim) that the Fed chooses to raise rates meaningfully above zero in the next year, starting in September.
But to some degree, the market has been discounting higher forward rates for a very long time. It has been consistently wrong on that point, but the steeply sloped yield curve (the 2y/10y spread hasn’t been flatter than 120bps since early 2008 – see chart, source Bloomberg) implies higher forward rates.
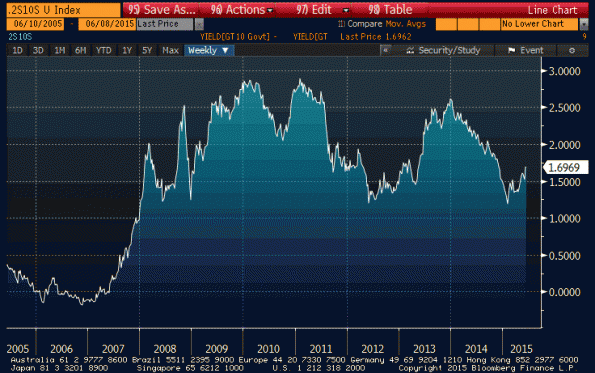
The rise in yields, in my view, is partly related to the prospect for changes in central bank policy, but also partly (and more sinisterly) related to the continuing intentional destruction by policymakers of the ability of large banks and dealers to make markets. We see worse liquidity in more and more markets almost by the day (as predicted five years ago in this space, for example here and here, as well as by many other observers).
Less liquid markets tend to trade with more volatility, as it gets harder to move institutional size, and at lower prices since holders of assets need to factor in the difficulty of selling a position. Higher yields are going to happen in any event, and when institutional holders of bonds decide to diversify into commodities or into other real assets, interest rates could rise quickly depending how quickly that meme spreads. Of course, the same is true of equities, and commodities. Asset-allocation shifts will get messier.
I actually think this isn’t a bad time tactically to enter long positions in fixed-income. The Fed isn’t going to be as aggressive as people expect; also, bonds will get some support from investors fleeing fading momentum in stocks. The chart below (source: Bloomberg; Enduring Investments calculations) shows the 52-week price change in stocks (via the S&P 500). This is one measure of momentum, and a very important one as lots of investors look at their returns in annual chunks. Incredibly, since the latter part of 2012, investors have always been able to see double-digit returns from stocks when they looked in the rear-view mirror. Today, that number is 7.5%.
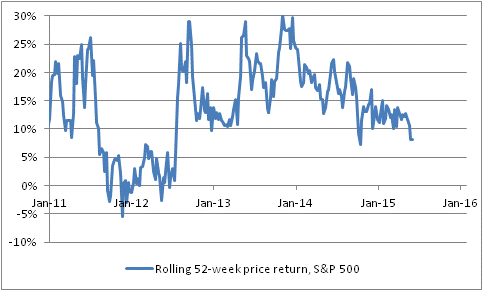
That’s still a terrific real return of more than 5%, but (a) many investors have very screwy return expectations, (b) many investors are well aware that they’ve been living on borrowed time with a liquidity-inspired rally, and (c) certain quantitative investors place significant weight to momentum, over value, in their investment models.
It’s just another red flag for stocks, but it has become passé to point them out. From the standpoint of a bond investor, though, this is good news because all of those equity owners, when they decide to take their chips off the table, will become bond buyers.
And when that happens, the liquidity issues in fixed-income might cut the other way for a while.
