Last year—when the COVID-19 pandemic hit—both the Federal Reserve and the U.S. government began aggressively easing. (Via borrowing and printing trillions at a pace never seen before).
And, since then, the mainstream financial media’s constantly pushed headlines about pro-longed inflation. Well, it's a year later—and the inflation scare has only grown. . .
For instance: many have highlighted the recent core-consumer price index (aka the core-CPI—a measure for consumer prices minus food and energy) which had its largest yearly increase in decades.
Or that higher commodity prices have caused global shipping rates—like the Baltic Dry Index (a measure of the cost for moving raw materials) to soar.
And on and on.
Such news has only reinforced the market’s prevailing bias that there is an inflationary wave coming.
So – what’s the issue?
Well, I’m skeptical of the crowd’s forecasts. And believe that the inflation trade is greatly overcrowded (putting investors in a fragile position).
Don’t forget—both the mainstream financial media and global central bankers have grossly underestimated how difficult it is to get inflation going in the ‘age of surpluses’ (aka the globalization and technology era) which began in the mid-1970’s.
And—just like previous cycles—I believe that they’re discounting this fact again. . .
Thus, I believe that this is just a temporary spurt of inflation (driven by supply-chain issues, base effects, and the economy re-opening). And that the long-term deflationary trend is still more likely to continue than not.
Let me explain. . .
First off: the surge in consumer prices was driven by just a few cyclical areas.
According to Guggenheim Investments, the sharp increase in the recent core-CPI was largely due to just a handful of categories. All of which were directly linked to the economy re-opening.
For instance: over-half the entire increase came from these four categories—used car prices, vehicle rentals, hotel rates, and airfare—which only make up ~5% of the core-CPI’s total index weight. . .
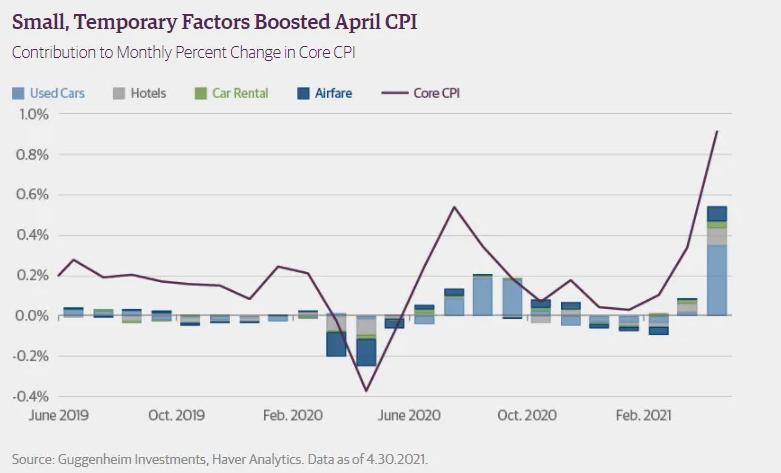
Note that it’s important to remember when car prices plunged -25% during the pandemic in early-2020, big rental companies rushed to liquidate their auto-fleets by dumping vehicles into the used car market.
But now—as demand recovers—the same firms have desperately been buying to rebuild their fleets. Pushing prices significantly up.
(Note that such reflexive cycles—aka feedback loops—are common during boom-busts periods. Meaning: in a bust, firms liquidate to try and raise cash when prices are already falling, thus amplifying further selling and price declines. And in a boom, firms re-stock when prices are rising, trying to build capital, amplifying further buying and price increases).
Thus, over the coming months, as the economy re-opens and supply bottlenecks unclog, it’s unlikely that such sharp price increases will continue.
Or—putting it another way—the above-trend price changes won’t sustain. And are bound to revert to their long-term mean.
Now – Second off: the U.S. has a large amount of idle capacity just waiting for any burst of ‘pent-up-demand.’
Take a look at the capacity utilization rate (aka the measure of potential output vs. realized output). It’s currently sitting at 75%—a multi-decade low.
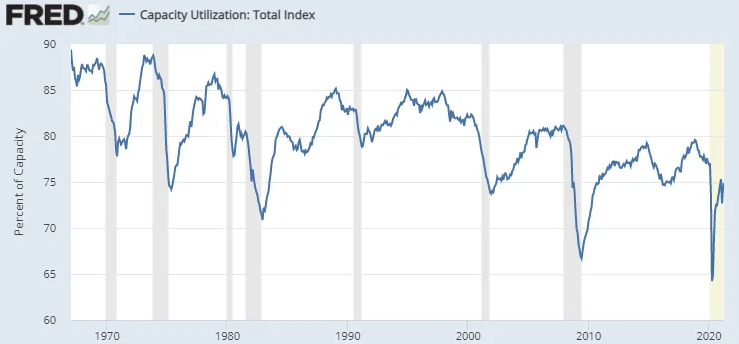
This indicates that there’s a significant amount of slack (aka excess capacity) in the economy. (Due to years of firms over-investing and expanding capacity— which has greatly outpaced demand).
Or, to put it simply: there’s far too much potential supply and not enough demand. . .
(Note that ‘zombie’ firms—companies dependent on low-interest rates and subsidies to survive—add to this supply glut issue).
Also, keep in mind that in the inflationary period in the 1970’s, the capacity utilization rate was at 90%. Which indicated supply shortages, thus pushing prices higher as demand overwhelmed suppliers.
But today it’s the opposite of the 1970’s. . .
Meaning: if prices continue rising, there’s a significant amount of idle capacity ready to quickly come online and dump supply onto the market (aka producers looking to benefit from the extra profits will turn on their idle capacity—soaking up any price increases by flooding the market with goods).
And true—while there’re many supply-bottlenecks globally due to an uneven re-opening, which have pushed prices up—these aren’t permanent.
Just take a look at the chart below. . .
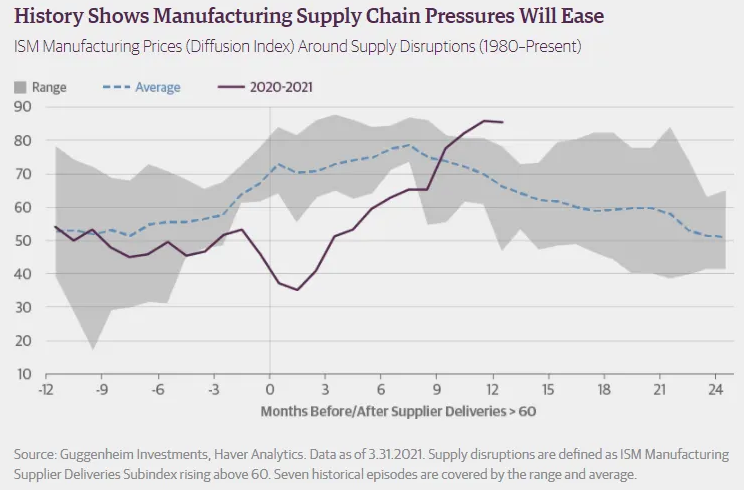
As history shows, such supply-side issues don’t last very long.
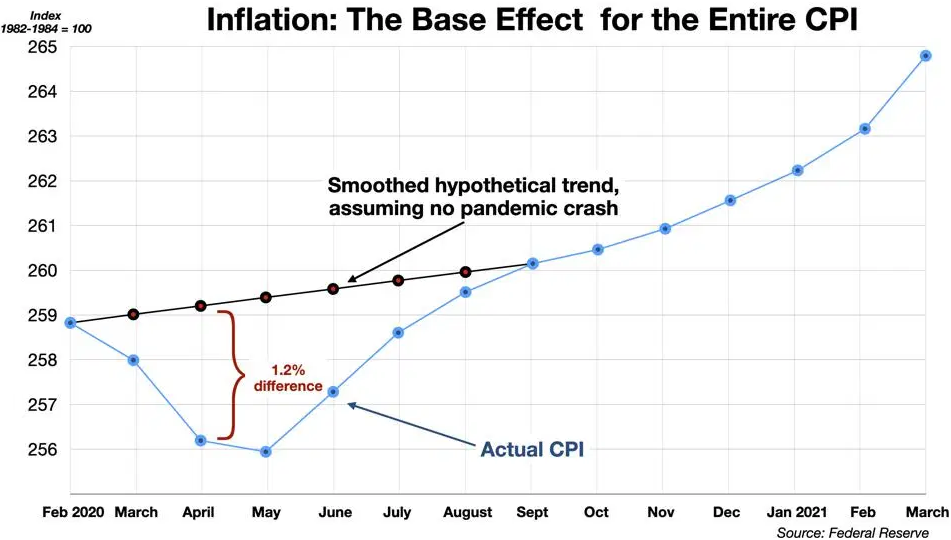
Finally – Third off: due to the sharp deflation in 2020 because of the global shutdown—there’s been artificially higher inflation in 2021 due to base effects (aka the rate of change between two data points and time).
Or, to put it another way, the big inflation numbers showing up recently are partly due to the exceptionally low numbers last year. . .
To give you some context: the pandemic had essentially killed economic activity last year, leaving demand anemic. And thus weighing down prices and the CPI.
Thus, because the CPI was so low last year (April 2020), even just a small increase in prices would push this years (April 2021) CPI much higher–artificially increasing the year-over-year inflation rate.
Putting it simply—if there hadn’t been deflation last year in 2020 due to the pandemic, then the headline CPI in April 2021 would’ve only shown a 2.9% year-over-year gain (vs. the 4.2% inflated rate it really was) . . .
Now, since humans are driven by cognitive flaws, such as the recency bias—aka believing recent events will continue far into the future (I’ve written more about this bias, read here)—the crowd’s busy pricing in higher inflation far into the future.
But base effects work both ways. Meaning that the artificially higher inflation in 2021 will most likely revert to artificially lower inflation in 2022 (aka the higher inflation numbers this year are the seeds for next years deflation). . .
So—in summary—I don’t believe in the inflation hype.
I expect the long-term structural trend (via low growth, low rates, deflation) to continue until there’s a forced rebalancing in the global economy. (More on this later).
The age of globalization and technology has been extremely deflationary. Keeping consumer prices exceptionally low (even with all the trillions central bankers have printed).
Unfortunately, the side-effect of this structural deflation has forced the global central bankers to keep their foot on the gas. Pumping enormous amounts of money into the system. (Remember—deflation is a tax on debtors and taxpayers. Thus since the world’s in a huge debt bubble any deflation can’t be allowed by the elites.)
But the problem is—instead of getting any price inflation—all this easy money has only fueled mal-investments, asset bubbles, further wealth inequality, increased market volatility, and bogged down future generations with excess debt.
All this makes the financial system far more fragile—increasing downside risk from potential future black swan events. . .
Now, could inflation run hotter for longer? Absolutely. Anything can happen.
But I’m doubtful. I believe that the above-trend inflation is due to short-term economic re-openings. And will inevitably revert lower to its long-run deflationary mean.
Remember: the economy only re-opens once. . .
PS: here’s an excellent and easy-to-read book on the deflationary forces in the economy: ‘The Price of Tomorrow: Why Deflation is the Key to and Abundant Future’ by Jeff Booth.
