In November of last year, Netflix Inc. (NASDAQ:NFLX) (~$355/share) landed in the Danger Zone after rising 363% year-to-date on promising quarterly results and much media hype. The stock rose rapidly for a while after our pick but has come back down nearly 20% in the past month.
Early last month, Netflix filed their annual 10-K, allowing us to update our model with its most recent financial data. While 2013 was a positive year for Netflix in some respects, many of the concerns in my November article were confirmed. Margin compression, fierce competition and high content costs are all hindering the already unrealistic profit growth priced into Netflix’s stock. Our original sell/short thesis is proving true as more evidence mounts that the NFLX business model is fundamentally broken.
Underlying Fundamentals Are In Decline
After Netflix’s rocky 2012, it was easy for the company to improve its performance in 2013. Netflix grew after-tax profits (NOPAT) from $33 million to $148 million, and grew its NOPAT margins from 1% to just over 3%. In addition, Netflix’s return on invested capital (ROIC) rose from 2% to 7%.
In general, this would be excellent performance for most companies, but considering Netflix’s track record before 2012 and its current valuation, the company is underperforming. In 2009, Netflix earned a NOPAT of $119 million. That means over the past five years NFLX has grown NOPAT by just $29 million, or just 4% compounded annually. This slow profit growth is largely due to two factors: rising content costs and the decline of Netflix’s high-margin DVD rental service.
Business Model is Busted
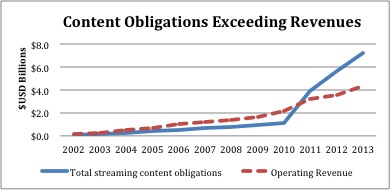
Judging by Netflix’s 2013 annual report, it does not look like either of these trends will reverse in the future. Figure 1 shows how the total value of NFLX’s obligations for streaming content has surpassed its annual revenue.
Netflix is seeing decreasing returns on capital as its costs rise. Since 2009, Netflix’s revenues have grown by 27% compounded annually while its costs of revenue have grown by 30% compounded annually. This disparity increases as the timeframe grows shorter: over the past two years, the company’s revenues have grown by 17% compounded annually, while its costs have grown by 23% compounded annually.
These rapidly increasing costs are primarily due to the licensing fees required to maintain Netflix’s expansive streaming content library. Netflix is in constant content-bidding wars with a number of other big name companies such as Amazon.com Inc. (NASDAQ:AMZN), Apple Inc. (NASDAQ:AAPL), Google Inc. (NASDAQ:GOOG) and Outerwall (OUTR). As a result, the costs of its large and frequently updated content library are rising quickly. To illustrate, streaming content obligations ballooned from $3.9 billion in 2011 to $7.3 billion in 2013. Amortization expenses on Netflix’s streaming library are following suit and grew $699 million to $2.1 billion over the same period.
Last November, we predicted that Netflix’s bottom line would find itself in trouble as costs rise because creating original content and hosting a content library are extremely expensive. Netflix is merely a delivery platform, hardly unique anymore. The company has many competitors now, many of whom are much better competitively positioned. For example, Amazon.com just announced a streaming television and music service in the same vein. Even a few unknown developers from Argentina can whip up a similar delivery service as a project.
Moreover, NFLX’s domestic DVD segment experienced membership losses of 56% in 2013, compared to a 26% decline from 2011 to 2012. While a decline in this business segment is hardly surprising considering both the increased competition of OUTR and the convenience of Netflix’s streaming services, it is financially damaging as Netflix’s DVD rental service has operating margins approaching 50%.
The decline of Netflix’s highly profitable DVD segment has been a drag on its previously explosive profit growth. Between 2003 and 2008, when Netflix first introduced its streaming video service, NOPAT grew by 73% compounded annually. Between 2008 and 2013, NOPAT has grown by just 14% compounded annually.
The Flawed Bull Case
Much of the Netflix bull case rests on the opportunity for international expansion. It is true that Netflix’s international subscriber base grew by an impressive 79%, and it is also true that there is presently much room for growth here. However, the same cost and pitfalls I have described above are not exclusive to Netflix’s U.S. operations, and additional hidden costs exist in expanding to international markets.
Netflix admits in its filing that international expansion holds similar and additional costs as its domestic services, including: (1) accounting for alternative payment methods, (2) adapting to foreign intellectual property and licensing structures and (3) foreign tastes not matching up with domestic products that Netflix has already paid to license internationally. Lack of widespread broadband service and the marketing costs to build a subscriber base from zero will also drag down international margins initially. Indeed, Netflix admits that losses in the international segment are substantial as the firm drives membership growth from zero.
Valuation is Approaching the Stratosphere
While the above factors have put the brakes on Netflix’s profit growth, investors seem to have missed the memo that the company’s profit margins will be permanently lower. To justify its current price of ~$355/share, NFLX would need to achieve NOPAT margins of 6.2% and grow NOPAT by 25% compounded annually for the next 16 years. In short, NFLX would need to almost double its current margins in this highly competitive space while growing NOPAT at a consistently exceptional rate. These expectations are clearly inconsistent with the realities that NFLX’s margins are falling, not rising, and that growth is slowing — not accelerating.
Recent declines in the stock suggest the market is just starting to catch on to the reality of the company’s situation, but I would emphasize the phrase “just starting.” The stock still has much farther to fall. The company provides a great service at a reasonable price, but investors need look no further than 2011’s Qwikster spin-off and subscriber exodus to see what kind of effect price hikes have on Netflix’s business.
Netflix shares dropped 20% in March alone. It’s time for investors to get out while they still can. When this stock still had positive momentum investors might have overlooked its flaws, but now that the momentum is gone NFLX represents an attractive short opportunity.
Insiders Selling
Although NFLX has had quite the run-up in the past year, executives have apparently decided that it’s time to get off the train – and quickly. In the past six months, insiders have sold off over one million shares, or 45% of their holdings. If this level of dumping does not serve as a warning to investors, I am not sure what will.
Stay Away from Funds that hold NFLX
Investors should stay clear of the following ETFs and mutual funds, as they allocate heavily to NFLX and earn my Dangerous or Very Dangerous rating:
1. NASDAQ Internet Portfolio (PNQI.O): 4.3% allocation and a Dangerous rating.
2. Hennessy Technology Fund (HTECX): 4.1% allocation and a Dangerous rating.
3. DJ Internet Index Fund (FDN): 4.0% allocation and a Dangerous rating.
André Rouillard contributed to this report.
Disclosure: David Trainer is short NFLX. David Trainer and André Rouillard receive no compensation to write about any specific stock, sector, or theme.