The Bureau of Labor Statistics released the latest CPI data this morning. Year-over-year unadjusted Headline CPI came in at 1.06%, which the BLS rounds to 1.1%, down from 1.47% last month (rounded to 1.5%). Year-over-year Core CPI (ex Food and Energy) came in at 1.72% (rounded to 1.7%), down from last month's 1.89% (rounded to 1.9%).
Here is the introduction from the BLS summary, which leads with the seasonally adjusted data monthly data:
The Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers (CPI-U) decreased 0.4 percent in April on a seasonally adjusted basis, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported today. Over the last 12 months, the all items index increased 1.1 percent before seasonal adjustment.
As was the case in March, a sharp decrease in the gasoline index was the primary cause of the decline in the seasonally adjusted all items index. The fuel oil index also declined while the electricity and natural gas indexes increased; the net result was a 4.3 percent decrease in the energy index. The food index, unchanged in March, rose 0.2 percent in April.
The index for all items less food and energy increased 0.1 percent in April, the same increase as in March. The indexes for shelter, used cars and trucks, new vehicles, and tobacco all increased in April. These increases were partially offset by declines in the indexes for apparel, airline fares, and recreation.
The all items index increased 1.1 percent over the last 12 months, the smallest 12-month increase since November 2010. The index for all items less food and energy increased 1.7 percent over the span; this was its smallest 12-month increase since June 2011. The food index rose 1.5 percent while the energy index declined 4.3 percent. More...
The Briefing.com consensus forecast was for a seasonally adjusted MoM -0.2% for Headline and 0.2% Core.
The first chart is an overlay of Headline CPI and Core CPI (the latter excludes Food and Energy) since 1957. The second chart gives a close-up of the two since 2000.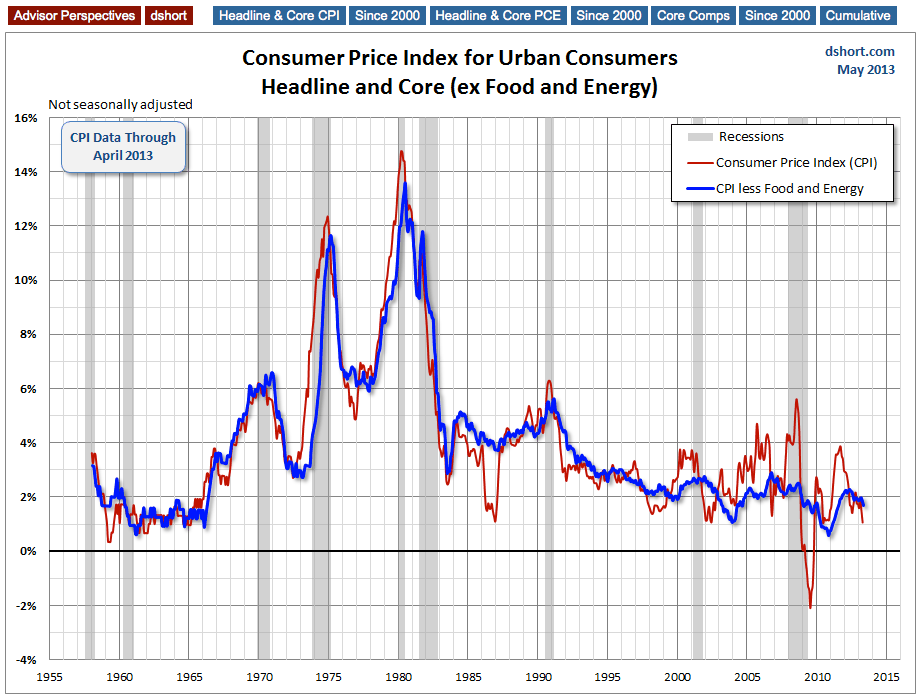
On the chart below I've highlighted 2-to-2.5 percent range. Two percent has generally been understood to be the Fed's target for core inflation. However, the December 12 FOMC meeting raised the inflation ceiling to 2.5% for the next year or two while their accommodative measures (low Fed Funds Rate and quantitative easing) are in place.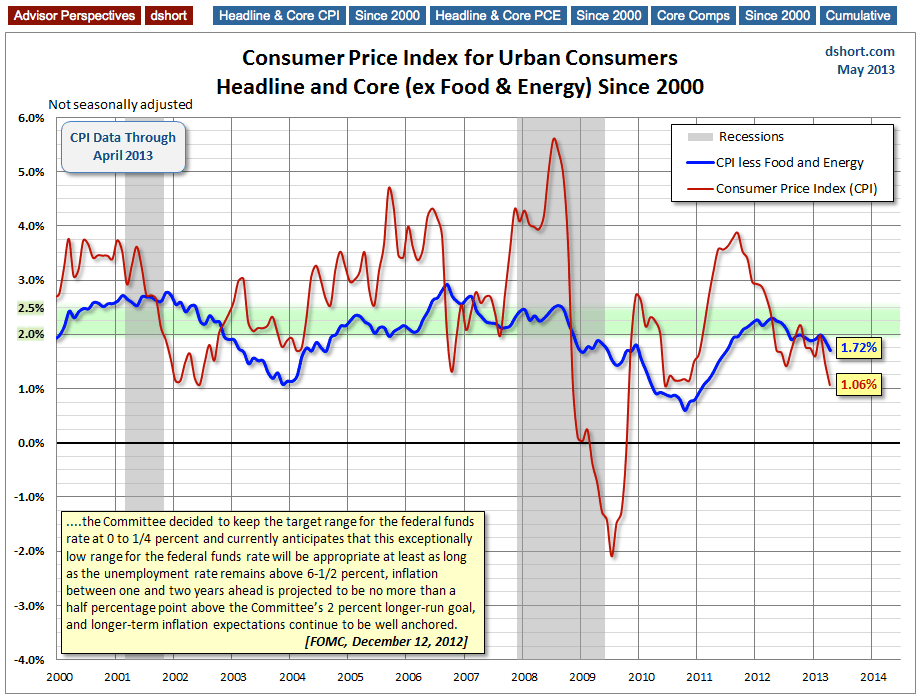
Federal Reserve policy, which has historically focused on core inflation, and especially the core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE), will see that the latest core CPI is below the near-term target range of 2 to 2.5 percent, and the more volatile headline inflation, is well below the target range.
- English (UK)
- English (India)
- English (Canada)
- English (Australia)
- English (South Africa)
- English (Philippines)
- English (Nigeria)
- Deutsch
- Español (España)
- Español (México)
- Français
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- Português (Portugal)
- Polski
- Português (Brasil)
- Русский
- Türkçe
- العربية
- Ελληνικά
- Svenska
- Suomi
- עברית
- 日本語
- 한국어
- 简体中文
- 繁體中文
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Bahasa Melayu
- ไทย
- Tiếng Việt
- हिंदी
Inflation Prints Below Forecast, Thanks To Lower Gasoline
Published 05/16/2013, 10:43 AM
Updated 07/09/2023, 06:31 AM
Inflation Prints Below Forecast, Thanks To Lower Gasoline
Latest comments
Loading next article…
Install Our App
Risk Disclosure: Trading in financial instruments and/or cryptocurrencies involves high risks including the risk of losing some, or all, of your investment amount, and may not be suitable for all investors. Prices of cryptocurrencies are extremely volatile and may be affected by external factors such as financial, regulatory or political events. Trading on margin increases the financial risks.
Before deciding to trade in financial instrument or cryptocurrencies you should be fully informed of the risks and costs associated with trading the financial markets, carefully consider your investment objectives, level of experience, and risk appetite, and seek professional advice where needed.
Fusion Media would like to remind you that the data contained in this website is not necessarily real-time nor accurate. The data and prices on the website are not necessarily provided by any market or exchange, but may be provided by market makers, and so prices may not be accurate and may differ from the actual price at any given market, meaning prices are indicative and not appropriate for trading purposes. Fusion Media and any provider of the data contained in this website will not accept liability for any loss or damage as a result of your trading, or your reliance on the information contained within this website.
It is prohibited to use, store, reproduce, display, modify, transmit or distribute the data contained in this website without the explicit prior written permission of Fusion Media and/or the data provider. All intellectual property rights are reserved by the providers and/or the exchange providing the data contained in this website.
Fusion Media may be compensated by the advertisers that appear on the website, based on your interaction with the advertisements or advertisers.
Before deciding to trade in financial instrument or cryptocurrencies you should be fully informed of the risks and costs associated with trading the financial markets, carefully consider your investment objectives, level of experience, and risk appetite, and seek professional advice where needed.
Fusion Media would like to remind you that the data contained in this website is not necessarily real-time nor accurate. The data and prices on the website are not necessarily provided by any market or exchange, but may be provided by market makers, and so prices may not be accurate and may differ from the actual price at any given market, meaning prices are indicative and not appropriate for trading purposes. Fusion Media and any provider of the data contained in this website will not accept liability for any loss or damage as a result of your trading, or your reliance on the information contained within this website.
It is prohibited to use, store, reproduce, display, modify, transmit or distribute the data contained in this website without the explicit prior written permission of Fusion Media and/or the data provider. All intellectual property rights are reserved by the providers and/or the exchange providing the data contained in this website.
Fusion Media may be compensated by the advertisers that appear on the website, based on your interaction with the advertisements or advertisers.
© 2007-2025 - Fusion Media Limited. All Rights Reserved.
