In the last week of November, the Ethereum network ran into operational problems that reveal potentially deep-rooted problems about its long-term survival. It all began with a seemingly simple blockchain game of breeding digital kittens, CryptoKitties. This insanely popular trading game running on the second largest-blockchain simply showed the world a large ignored underlying scaling issue that remains unsolved on Ethereum.
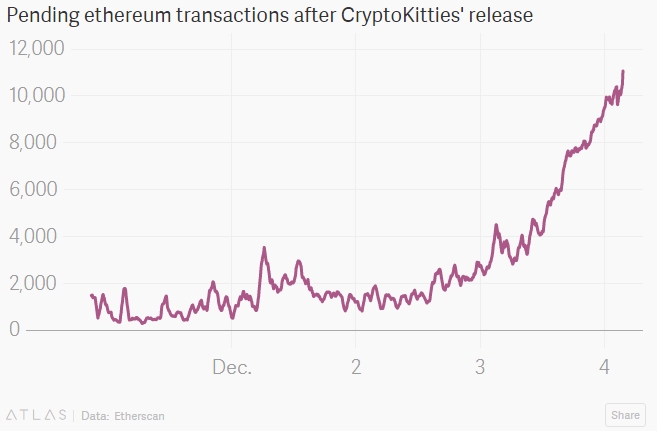
The simple game of breeding digital kittens that can be bought or sold using Ether caused the volume of unprocessed transactions on the Ethereum blockchain to jump about 600% in one week as seen in the chart below.
The massive increase the unprocessed transactions and the subsequent flash crash exposes the fact that the Ethereum blockchain is susceptible to serious downtime and congestion as the network continues to grow. Ethereum is becoming a victim of its own success as the first popular application on its blockchain has shown the ability to cripple the system.
The more worrisome problem is that stakeholders in the Ethereum network can't seem to agree on the best way to proceed with the fixing of the scaling problems. Earlier disagreements on how to support growth and scale led to the forking of Ethereum Classic (ETC) but it seems that investors must start to factor in the scaling risk into Ethereum investments going forward.
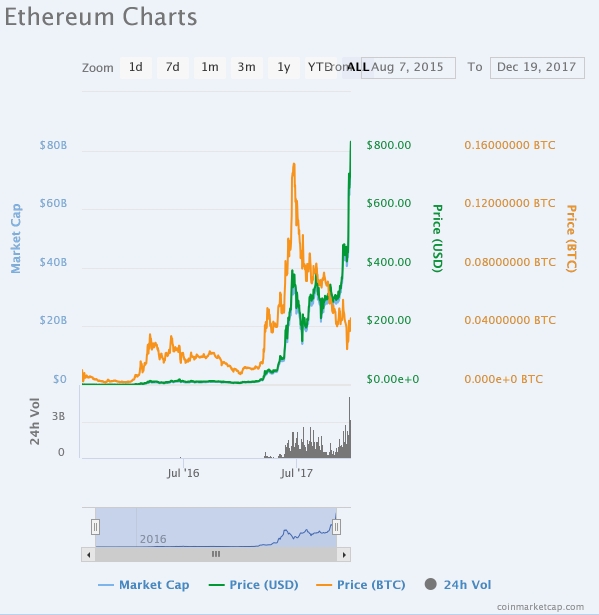
Nonetheless, there's no denying the fact that Ethereum has delivered more than 4000% gains this year and it currently trades around $831.
Nonetheless, Ethereum might plateau because of its scaling challenges the same way the huge value of Bitcoin might cap its transactional use. This post looks at potential challengers that could take Ethereum's place especially for building blockchain applications.
Qtum is one of the leading Blockchain technologies that could displace Ethereum or at the very least give Ethereum a worthy competition. Qtum is simply a blockchain platform that makes it easy for businesses to build decentralized apps that work on mobile devices while being fully compatible with existing blockchain ecosystems. Founded in 2016, Qtum has proven itself as a disruptor that has the potential to bridge the gulf between Bitcoin and Ethereum blockchain ecosystems.
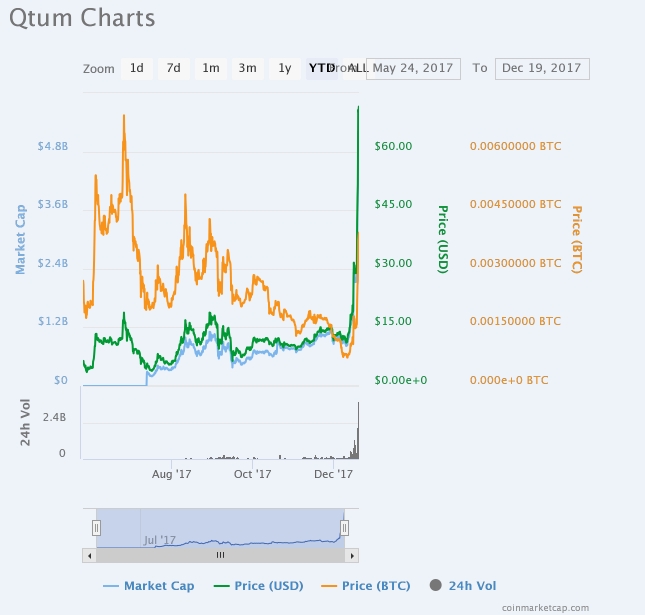
Investors will do well to note that Qtum has held a successful seed round where it raised $1M and a crowdsale where it raised another $15.6M. Post ICO, the Qtum token now trades up an incredible 23,743% at a trading price around $71.52 from an ICO price of $0.30 in May. The Qtum token also has a market cap of $3.15B making it the 13th biggest coin by market cap.
Fundamental to Qtum's tech, which gives it a possible lead over Ethereum is the superior X86 Virtual Machine, which has the ability to handle greater complexity than the Ethereum Virtual Machine. In addition, Qtum's tech is able to deliver on the security and privacy promise of Ethereum’s Byzantium upgrade.
Businesses seeking to get involved in the growing blockchain ecosystem will also like the fact that Qtum’s innovative Decentralized Governance Protocol provides smart contract developers with a standard set of functions that can be relied upon to ensure secure and correct code of optimum size, so that costs are controlled and known before runtime (when the code is executed).
Just last month, the Parity wallet on Ethereum suffered a hack that froze some 573 wallets and rendered them inaccessible. The hack led to the freezing of about $160 million worth of Ether and there's not much that the Ethereum Network can do to renew access to those funds even though the Parity team has acknowledged that the hack has led to much caused "distress and anxiety" within the community.
The hack that hit Parity could not happen with Qtum’s solution because Qtum simply boasts an improved development environment, which guards against writing inefficient smart contracts acts through ͞dependency indications͟ that explicitly points a smart contract to the other contracts it depends on to function.
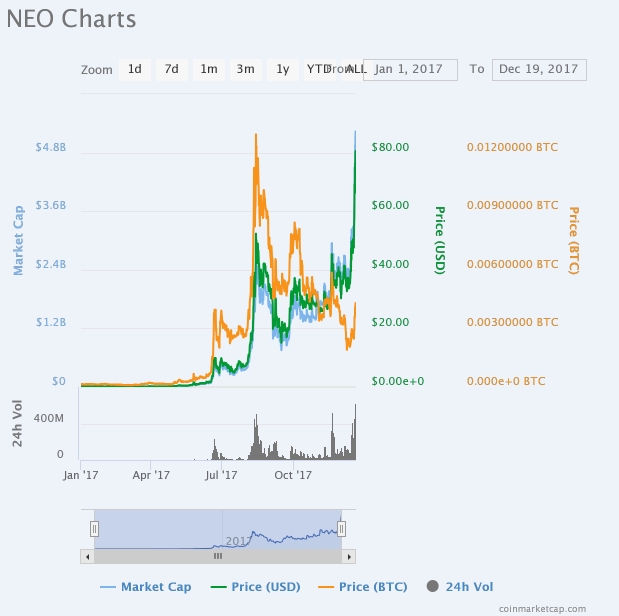
NEO, formerly Antshares has had an impressive rise to fame that is nothing short of monumental in the blockchain industry. From an ICO price of $0.036 in 2016 as Antshare, NEO now trades up around a trading price of $78.83. The cryptocurrency also has a coin market cap of $4.79B to earn the position of the 15th cryptocurrency by market capitalization.
Neo is essentially another smart contract blockchain platform and many investors refer to it as the Ethereum of China. NEO's value proposition stems from the fact that fact that it allows users to register, trade, and circulate different assets through a validated digital identity use scenario. Neo's Ethereum-like smart contracts ensure a digital, and bordereless smart contract solution that doesn’t require the centralized services of a third- party.
One of the reasons Neo is a strong contender to displace Ethereum is that it supports different additional code bases such as C#, VB.Net, F#, Java, and Kotlin; in contrast, Ethereum is limited to its own Solidity, which developers must learn before they can make stuff on the network. However, some investors are still worried about the commitment of NEO to keeping the network alive because NEO was 100% premine and the developers with pre-mined coins to dump their coins on the market.
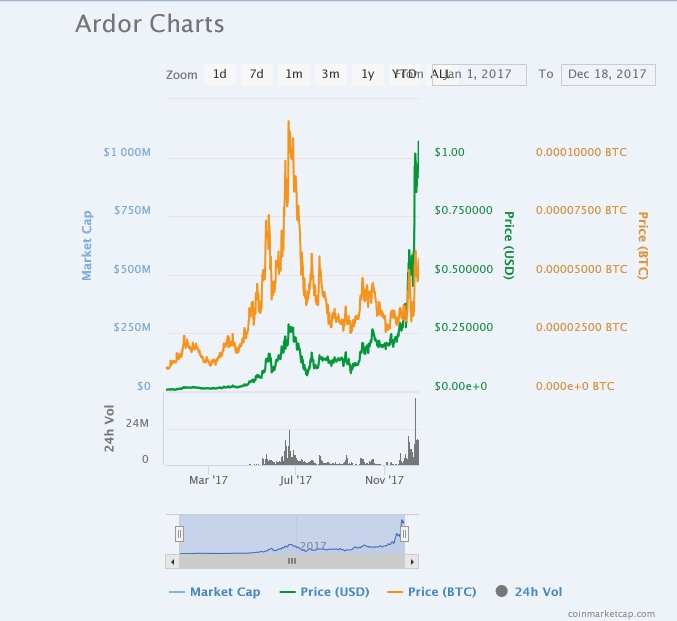
Ardor is another blockchain platform that has the potential to displace Ethereum as the go-to blockchain for the enterprise segment. In fact, businesses that need a Blockchain-as-a-service platform will find undeniable potential in Ardor's value proposition. Ardor will make it easy for businesses to create their own blockchains using parent-child chains instead of the bloated nodes of some of the popular blockchains.
Using the Nxt technology created by its parent company Jelurida, Ardor's blockchain simply has a main chain and a practically endless number of child chains. The main chain holds all Ardor token (ARDR) transactions but other features of the blockchain will be inaccessible in order to ensure improved performance and limit the odds of blockchain bloat. The child chains in turn are meant for businesses that want to create their own blockchain complete with tokens, aliasing, data cloud, account control, marketplace, and secure messaging among others.
Another key factor that gives Ardor's blockchain an edge over Ethereum is that Ardor uses a Proof-of-stake (PoS) network as opposed to a Proof-of-work (PoW) system that Ethereum uses. The Proof-of-stake system is resistance to potential censorship threat that could cripple the cryptocurrency industry because it doesn’t require heavy mining and the need for a mining factory. Interestingly, Ethereum has started to consider the idea of switching to a Proof-of-stake model; hence, Ardor is on the right path and with a first mover advantage over Ethereum.
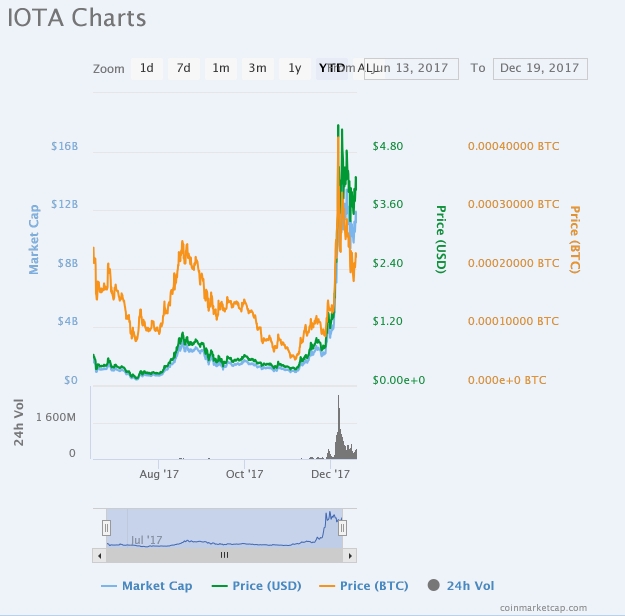
IOTA, which styles itself as the Blockchain backbone for the Internet of things (IoT) is another Ethereum competitor that is worthy of your attention. IOTA made its debut on the ICO scene about two years ago and it now trades around a modest $3.88. The cryptocurrency also has a coin market cap of $10.78B to earn the position of the 7th cryptocurrency by market capitalization. The simplest reason IOTA is a potential Ethereum killer s that it solves three big problems ailing the Ethereum Network: scalability, transaction costs, and online transactions.
Scalability on the IOTA network is already an inbuilt feature, which is designed to accommodate growth in the ecosystem. To begin with, every new transaction will verify two previous transactions on the network. Hence, as the IOTA network will see an increased growth and adoption, its blockchain becomes perpetually scalable with each new transaction.
The IOTA blockchain is also designed to enhance offline transactions with the use of subtangles, where offline transactions are recorded. The subtangles are then automatically reattached to the tangle when the node comes back online. In essence, IOTA nodes don't necessarily have to be online over the length of the whole process and transaction can still be carried when the node is effectively offline.
Which stock should you buy in your very next trade?
With valuations skyrocketing in 2024, many investors are uneasy putting more money into stocks. Unsure where to invest next? Get access to our proven portfolios and discover high-potential opportunities.
In 2024 alone, ProPicks AI identified 2 stocks that surged over 150%, 4 additional stocks that leaped over 30%, and 3 more that climbed over 25%. That's an impressive track record.
With portfolios tailored for Dow stocks, S&P stocks, Tech stocks, and Mid Cap stocks, you can explore various wealth-building strategies.