Last month, container counts were showing a significant surge (in imports and exports) – suggesting that economic growth MAY actually be showing signs of life. What a difference one month makes.
- Economically intuitive imports have collapsed in March (but are still growing year-to-date), and exports are down in March are now contracting year-to-date.
- This ties together with declining rail intermodal counts – and suggests the main street economy may be struggling.
Exports (which are an indicator of competitiveness and global economic growth) are down 6.9% year-over-year (versus last month’s +4.2%) – and down 11.1% month-over-month. Exports are now on a negative growth trend line.
There is reasonable correlation between the container counts and the US Census trade data also being analyzed by Econintersect. But trade data lags several months after the more timely container counts. From the graph below, it can be observed that exports (red line) have a slightly negative long term trend line over the last 3 years, whilst imports (blue bars) seem flat over the last year – but also have an improving 3 month trend.
Unadjusted Year-over-Year Change in Container Counts – Ports of Los Angeles and Long Beach Combined – Imports (red line) and Exports (blue bars)
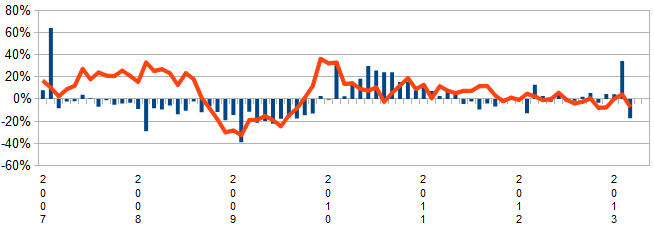
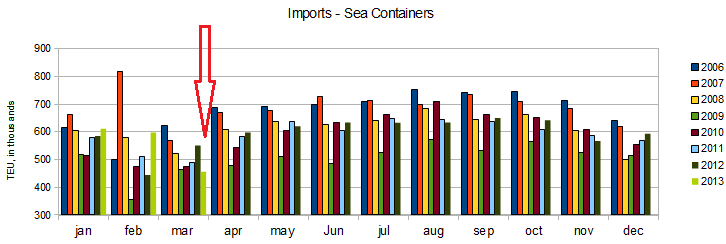
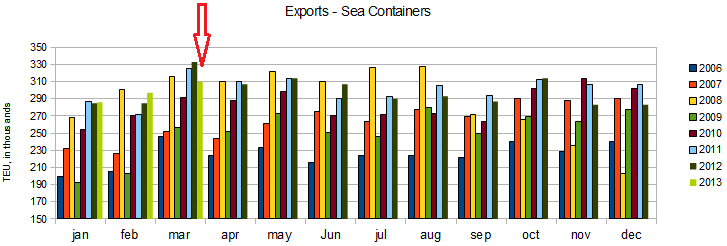
Econintersect considers import and exports significant elements in determining economic health (please see caveats below). the takeaway from the graphs below is that imports still have not returned to pre-2007 recession levels, while exports did recover (and now with a short term improvement trend).
Unadjusted Import Container Counts – Ports of Los Angeles and Long Beach Combined
Unadjusted Export Container Counts – Ports of Los Angeles and Long Beach Combined
o far in 2013 other major transport indicators are beginning to show economic growth.
- February Transport (January 2013): Up 4.2% year-over-year
- Rail (4 week average ending 06 April) up 0.0% compared to 4 week average one month ago, up 0.3% comparing 4 week moving average to the average one year ago
- Container Counts (February 2013): imports up 34.4% year-over-year, exports up 4.2% year-over-year.
The Ports of LA and Long Beach account for much (approximately 40%) of the container movement into and out of the United States – and these two ports report their data significantly earlier than other USA ports. Most of the manufactured goods move between countries in sea containers (except larger rolling items such as automobiles). This pulse point is an early indicator of the health of the economy.
Containers come in many sizes so a uniform method involves expressing the volume of containers in TEU, the volume of a standard 20 foot long sea container. Thus a standard 40 foot container would be 2 TEU.
There is a good correlation between container counts and trade data (the US Census trade data is shown on the graph below). Using container counts gives a two month advance window on trade data.
Inflation Adjusted Year-over-Year Change Imports (blue line) and Exports (red line)
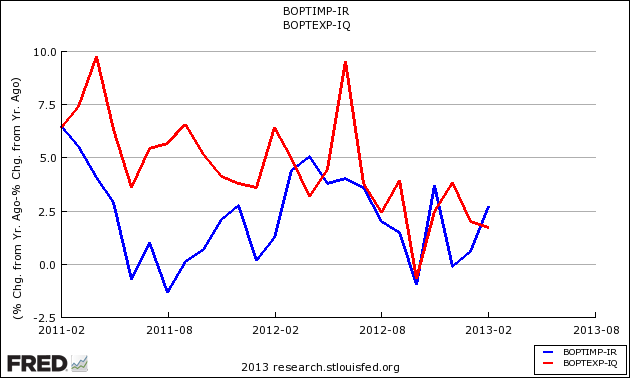
Transport has been languishing with very weak growth, but it appears transport may again be strengthening.
Caveats on the Use of Container Counts
These are extraordinary times with historical data confused by a massive depression and significant monetary and fiscal intervention by government. Further containers are a relatively new technology and had a 14 year continuous growth streak from 1993 to 2006. There is not enough history to make any associations with economic growth – and we must assume a correlation exists.
Further, it is impossible from this data to understand commodity or goods breakdown (e.g. what is the contents in the containers). Any expansion or contraction cannot be analyzed to understand causation.
Imports are a particularly good tool to view the Main Street economy. Imports overreact to economic changes much like a double ETF making movements easy to see.
Contracting imports historically is a recession marker, as consumers and businesses start to hunker down. Main Street and Wall Street are not necessarily in phase and imports can reflect the direction for Main Street when Wall Street may be saying something different. During some recessions, consumers and businesses hunkered down before the Wall Street recession hit – and in the 2007 recession the contraction began 10 months into the recession.
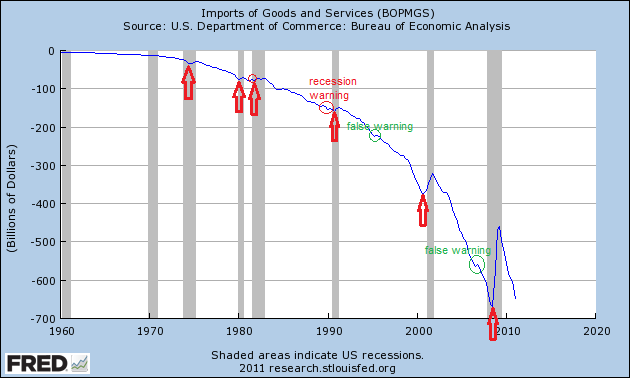
Above graph with current data:
Imports of Goods and Services
Econintersect determines the month-over-month change by subtracting the current month’s year-over-year change from the previous month’s year-over-year change. This is the best of the bad options available to determine month-over-month trends – as the preferred methodology would be to use multi-year data (but the New Normal effects and the Great Recession distort historical data).
